 MU
MUmshaarif490@gmail.com
Remote Desktop
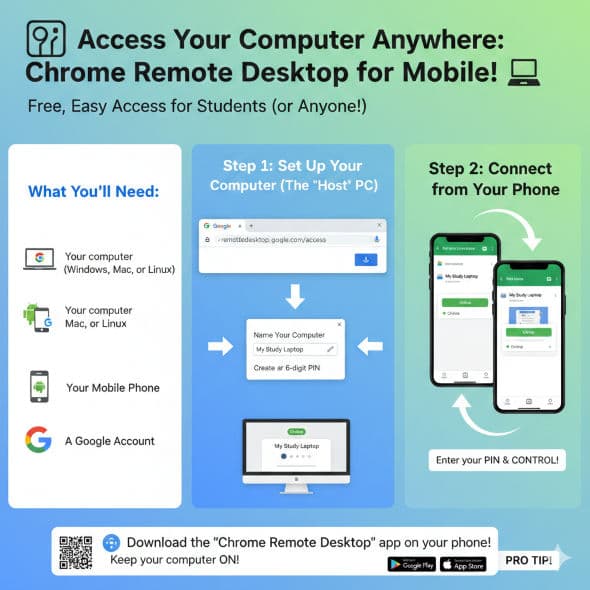
📱 Access Your Computer Anywhere: Chrome Remote Desktop for Mobile! 💻
Hey everyone! Ever needed a file from your home computer but you're out and about with just your phone? Or maybe you want to quickly check something on your desktop from bed? Chrome Remote Desktop is a FREE, super easy solution for students and anyone who needs quick remote access without a "work or school account" or complicated setup.
This guide will show you how to get your Windows or Mac computer accessible from your Android or iOS phone in minutes!
What You'll Need:
Your computer (Windows, Mac, or Linux) with Google Chrome installed.
Your mobile phone (Android or iPhone/iPad).
A Google Account (the same one signed in on both your computer and phone).
An internet connection on both devices!
Step 1: Set Up Your Computer for Remote Access (The "Host" PC)
This is a one-time setup on the computer you want to control.
Open Google Chrome on your computer.
Go to the Chrome Remote Desktop website: remotedesktop.google.com/access
Download the Host Software: Click the blue download button (it looks like a down arrow) next to "Set up remote access."
Follow the prompts to download and install the Chrome Remote Desktop Host installer for your operating system. This is crucial for enabling your computer to be remotely controlled.
Name Your Computer: Once the host software is installed, you'll be prompted to give your computer a name. Choose something easy to remember (e.g., "My Gaming PC," "Study Laptop").
Create a PIN: You'll then be asked to create a 6-digit PIN. This is like a password specifically for Chrome Remote Desktop. Write it down! You'll need it every time you connect.
Tip: Use a strong, unique PIN you haven't used elsewhere.
Enable Remote Access: After setting the PIN, your computer will now be listed under "Remote Access" on the remotedesktop.google.com/access page with a green "Online" status. Great job!
Step 2: Connect from Your Mobile Phone (Android & iOS)
Now for the fun part – accessing your computer from your phone!
Download the Mobile App:
For Android: Search for "Chrome Remote Desktop" on the Google Play Store and install it.
For iOS (iPhone/iPad): Search for "Chrome Remote Desktop" on the Apple App Store and install it.
Open the App: Launch the "Chrome Remote Desktop" app on your phone.
Sign In: Make sure you're signed in with the SAME Google Account you used on your computer.
Select Your Computer: You should see the name of your computer listed that you set up in Step 1. Tap on it.
Enter Your PIN: You'll be prompted to enter the 6-digit PIN you created earlier.
Optional: You can check "Remember my PIN" for quicker access next time.
Connect! You should now see your computer's desktop on your phone screen!
🎉 You're Connected! What Now?
Pinch to Zoom: Zoom in and out on your desktop.
Tap to Click: Tap anywhere to perform a mouse click.
Scroll: Use two fingers to scroll.
Keyboard: Tap the keyboard icon to bring up your phone's keyboard.
Menu (Swipe from side): Access options like disconnecting, switching monitors, or sending Ctrl+Alt+Del.
Pro Tip: Keep Your Computer On!
For Chrome Remote Desktop to work, the computer you're trying to access must be powered on and connected to the internet. If it goes to sleep or shuts down, you won't be able to connect remotely.
That's it! You now have a powerful tool to access your files and applications on your main computer from anywhere, directly from your mobile device. Happy remote computing!
Languages Age
HTML is 30 years old.
CSS is 29 years old.
JavaScript is 28 years old.
PHP is 30 years old.
MySQL is 30 years old.
WordPress is 22 years old.
Bootstrap is 14 years old.
jQuery is 19 years old.
React is 12 years old.
Angular is 14 years old.
Vue.js is 11 years old.
Node.js is 16 years old.
Express.js is 15 years old.
MongoDB is 16 years old.
Next.js is 9 years old.
Tailwind CSS is 8 years old.
Vite is 5 years old.
What's your age?
The Humble Birth of the World Wide Web
Before Google, Facebook, or even graphic browsers, the entire World Wide Web was hosted on one single computer—and it came with a dire warning! ⚠️
In late 1990, at CERN in Switzerland, British scientist Tim Berners-Lee used a NeXT computer to develop the Web. This machine, the world’s first-ever web server, had a handwritten note taped to it that famously read: "THIS MACHINE IS A SERVER. DO NOT POWER IT DOWN!!"
Imagine the fate of the modern world resting on a single plug! 🤯
The Vision: Berners-Lee first proposed his "vague, but exciting" information management system in March 1989.
The Launch: On December 20, 1990, the first simple website—explaining the Web itself—was published on this very machine.
The Explosion: The Web didn't truly take off until the first public invitation was posted in 1991, followed by the release of the user-friendly Mosaic browser in 1993. By 1996, there were over 100,000 websites, fundamentally changing how humanity shares information.
We owe our digital lives to this one machine and the brilliant mind that made it all possible.
#WorldWideWeb #TimBernersLee #TechHistory #CERN #Innovation
Generative AI do not understand things the way humans do
Even though the outputs feel thoughtful or creative, the model is *not thinking*.
It’s recognizing patterns, predicting the next likely word, pixel, or sound based on everything it has seen before. 🤖
*But here’s the surprising part: 👀*
It *does* build an internal representation of concepts, almost like a mental space 🧭🧩
Inside the model, words/ideas are stored as *vectors* (basically coordinates in high-dimensional math space).
And these vectors map relationships between concepts
_For example:_
*Concept* - AI “understands” it as…
1. *Paris* - coordinates near *France, Europe, capital*
2. *Dog* - coordinates near *animal, pet, loyal*
3. *Freedom* - coordinates near *rights, choice, autonomy*
That’s why the famous analogy works:
> 👑 *King* - 👨 *Man* + 👩 *Woman* ≈ 👸 *Queen*
Not because AI knows royalty or gender - but because the relationships between these concepts are stored *mathematically* in the same shape
So AI doesn’t *think*...
But it *models the structure of thought*. 🧠📊
It’s kind of like:
It doesn’t know what *fire* feels like
But it knows how “fire” appears in stories 📖, physics explanations ⚛️, metaphors ✍🏽, survival guides 🧯, and poems 📝 ...
So it can *speak about it convincingly*.
*The Insight:*
Generative AI doesn’t have consciousness.
But it has a very accurate *map* of how humans use and connect ideas
_It’s like:_
> 🪞 No mind, but a mirror of millions of minds.
ChatGPT will no longer give personal health or legal advice It will only explain general information
That change is primarily due to *safety, ethical, and legal concerns*. Here's why:
1. *Accuracy & Liability*: Health and legal issues are serious and often require context, nuance, and professional expertise. If ChatGPT gives incorrect advice in these areas, it could lead to harmful decisions. To avoid causing harm and potential legal liability OpenAI restricts such guidance.
2. *Not a licensed professional*: ChatGPT is not a doctor or lawyer. It can’t assess personal conditions, understand legal history, or provide tailored professional advice. That’s why it's now limited to explaining general concepts only.
3. *Encouraging proper support*: The goal is to push users to consult *real, qualified professionals* who can offer accurate, contextual, and responsible help rather than relying on AI alone.
So, ChatGPT can still help explain medical or legal terms, processes, or general principles but won’t give personal diagnoses, treatment suggestions, or legal strategies.
50 Must Know Python Concepts for Interviews
📍 *Python Basics*
1. What is Python?
2. Python 2 vs 3
3. Variables & Data Types
4. Operators
5. Type Conversion & Casting
📍 *Control Flow*
6. if-else statements
7. for & while loops
8. break, continue, pass
9. Ternary operator
10. List comprehensions
📍 *Functions & Scope*
11. Defining functions
12. *args & **kwargs
13. Global vs Local scope
14. Lambda functions
15. Recursion
📍 *Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)*
16. Classes & Objects
17. Constructor (_init_)
18. Inheritance
19. Encapsulation
20. Polymorphism
📍 *Exception Handling*
21. try-except-finally
22. raise keyword
23. Custom exceptions
24. Common errors (TypeError, ValueError, etc.)
25. Assertions
📍 *Data Structures*
26. Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dicts
27. List vs Tuple
28. Set vs Frozenset
29. Dictionary methods
30. Iterating over data structures
📍 *Strings & Files*
31. String methods & slicing
32. f-strings & formatting
33. Reading & Writing files
34. Context Managers (with)
35. JSON handling
📍 *Advanced Python*
36. Decorators
37. Generators & yield
38. Iterators & Iterable
39. Modules & Packages
40. Virtual Environments (venv)
📍 *Libraries & Tools*
41. NumPy / Pandas basics
42. Regular Expressions (re)
43. Requests (API calls)
44. Logging
45. Unit Testing (unittest/pytest)
📍 *Interview Essentials*
46. List vs Set vs Dict performance
47. Shallow vs Deep copy
48. Mutable vs Immutable
49. Pythonic code best practices
50. Version control (Git + GitHub)
YouTube Networking Courses
Top 15 Networking Courses on YouTube:
1. FortiGate Firewall Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4ZOTbg97jiWkT0mMZk9OzY&si=KSdkar442h4zGFQt
2. PaloAlto Firewall Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6NNKtNtrZT1l5FAG9ZX-vh&si=hu4FB_daADNSXQ3U
3. ASA Firewall Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4ToJQTLHmqgkh_vQW7IGyE&si=a17cN_vx9I9NfmBk
4. Cisco SD-WAN Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6ff2XWiiRT3ZNjIR7S0YlM&si=DPC254FTFbwyNeSO
5. Enterprise Network Configurations Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4-0zyoQ5xomOLIN-VidhU0&si=xgHtQveP9XF8ZXRW
6. Network Troubleshooting Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4nFSy1qGaXPhsSLrdl53SV&si=nA1Y21cMoHdHkOHJ
7. Network Switching Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6OW48mZb2GlBd-qHrBI32l&si=a61Z3_RB7UvgbZsI
8. Wireless Networking Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6wvS47W1d_90IQFR2r2Q0m&si=WO_O686HNewGiV8N
9. Master MPLS Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4eKco3y4b2iTVbo4H0dnOg&si=6oMn-koPmax0ixln
10. Enterprise Troubleshoot Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6GOAo40ZPIH1bp3FAzFqFl&si=gNPVPZqn2nitECjf
11. OSPF Full Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn7zgoSR7vjUYA44yzx8xvnf&si=slGRGA6lFr6OQv5v
12. IPv6 Full Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6UfS4DcMF0cmPTTgYxApQT&si=7OJEmFG0w7LMGkbr
13. BGP Full Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn6dr8VyA1bNIiEsjkU3YG-X&si=afTq1xYK9eL0Hocl
14. Real-Time Configurations Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn4QoMKmdl6KYQZSxosw-wuq&si=AAhKZ_zerbApqqO4
15. VPN Full Course
https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLmgyxPj-5jn7knP3rq1k2UiDRSJNh7bU1&si=3kAnNON82ghexZlK
10 Cybersecurity Tips Everyone Should Follow
✅ *10 Cybersecurity Tips Everyone Should Follow* 🔒💻
1️⃣ Use strong, unique passwords for every account.
2️⃣ Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
3️⃣ Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments.
4️⃣ Keep your software, apps, and OS updated.
5️⃣ Use secure Wi-Fi and a VPN on public networks.
6️⃣ Regularly back up important files.
7️⃣ Monitor your accounts for unusual activity.
8️⃣ Avoid sharing personal info on untrusted sites or apps.
9️⃣ Be cautious with AI/chat platforms — never share sensitive data.
🔟 Educate yourself on phishing and online scams.
📌 *Safety first — small steps protect you big time!*
💬 *Tap ❤️ if you found this helpful!*